Blog
Brise Chemicals > Blog > Uncategorized > Why is Green Hydrogen an important source of energy for human life?
Why is Green Hydrogen an important source of energy for human life?
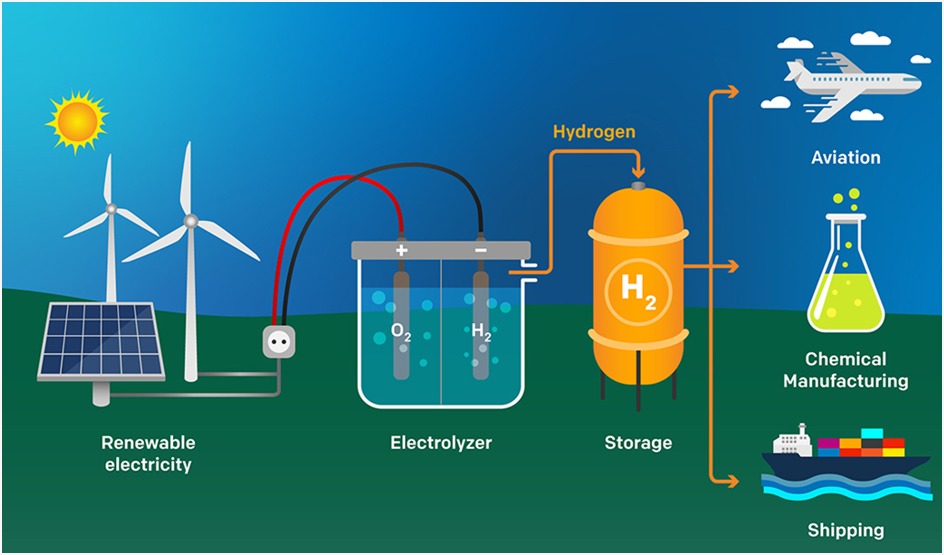
Green hydrogen is an important source of energy for human life as it has the potential to provide a clean and sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. Fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, are the primary source of energy for the world today, but they have significant drawbacks. They contribute to climate change by releasing greenhouse gases, and they can have negative impacts on air quality and human health. Green hydrogen, on the other hand, is produced using renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power, which do not emit greenhouse gases.
Green hydrogen can be used in a wide range of applications.
Including transportation, heating, and electricity generation. One of the most promising uses of green hydrogen is in transportation. It can be used to power vehicles such as cars, buses, and trains, offering a clean and sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles have already been developed, and as the technology improves, they have the potential to replace conventional vehicles.

Another important use of green hydrogen is in industry. Many industries require high-temperature heat for processes such as steel and cement production, which currently rely on fossil fuels. Green hydrogen can offer a clean and sustainable alternative that can significantly reduce carbon emissions from these industries.
Green hydrogen also has the potential to provide energy security and independence for countries that do not have access to fossil fuel resources. For example, countries that rely heavily on oil imports could potentially use green hydrogen to power their transportation and industrial needs, reducing their dependence on foreign oil.
Green hydrogen can create new economic opportunities.
Moreover, the adoption of green hydrogen can create new economic opportunities and jobs in the renewable energy sector. As demand for green hydrogen increases, new industries and businesses will emerge, creating jobs in manufacturing, research, development, and deployment.
The widespread adoption of green hydrogen, however, is not without its challenges. The production of green hydrogen requires significant amounts of energy, and the cost of producing it is currently higher than that of fossil fuels. However, with advancements in technology and economies of scale, the cost of producing green hydrogen is expected to decrease. Another challenge is the storage and distribution of green hydrogen. Hydrogen is a highly flammable gas, and storing it can be dangerous if proper safety measures are not in place. Additionally, the infrastructure required to transport and distribute green hydrogen is not yet fully developed, although there are ongoing efforts to address this challenge.
In conclusion, green hydrogen is an important source of energy for human life as it offers a clean and sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. It has the potential to reduce carbon emissions, improve air quality, and promote energy security and independence. However, the adoption of green hydrogen requires significant investment in research, development, and infrastructure. If we can overcome these challenges, we can build a more sustainable future and ensure a healthy planet for generations to come.

